Starlink bypass mode
Introduction
I am experimenting with Starlink, which provides internet connection services using low orbit satellites at an altitude of 550 kilometers. I suspended my starlink service since May of this year, restarted. Then, I try using Starlink remotely with a VPN (virtual private network) installed in a remote location with few obstacles. Although this configuration may not be very practical, I believe it can be used to understand the characteristics of Internet connections by low-orbit satellites and to examine the possibility of positioning.
Pause and resume of use
Please note that I have a direct contract with Starlink in Japan. It is also possible to sign a Starlink usage contract through a reseller, but the contract may differ from the one below. I also did some research, and found that as IIJ’s Mr. Taniguchi mentioned (in Japanese), it is best to contract directly with Starlink. It seems advantageous. If you contract directly, for example, purchasing the Ethernet adapter option is also easy.
You can easily suspend and resume usage from the smartphone app connected to Starlink Wi-Fi or from the Starlink homepage. You can also remotely restart Starlink or fold the antenna.
Usage fees are normally charged for one month from the start date of use. Even if you apply for suspension, you can continue to use it until the original period, and it will be suspended on the next original start date.
However, reopening is possible at any time. From the restart date until the next billing date, you will be billed on a daily basis. Starlink does not require any maintenance fees during the suspension period or fees for resuming use. I’m very happy that I only pay for the amount I use to connect to the Internet.
Service plan
Currently, users can freely change their plans, and they have also added a priority usage plan with capacity restrictions and a menu for purchasing additional capacity. Previously, there were two plans: residential only and RV (recreational vehicle), and once you selected the RV plan, you could not switch back to the residential plan.
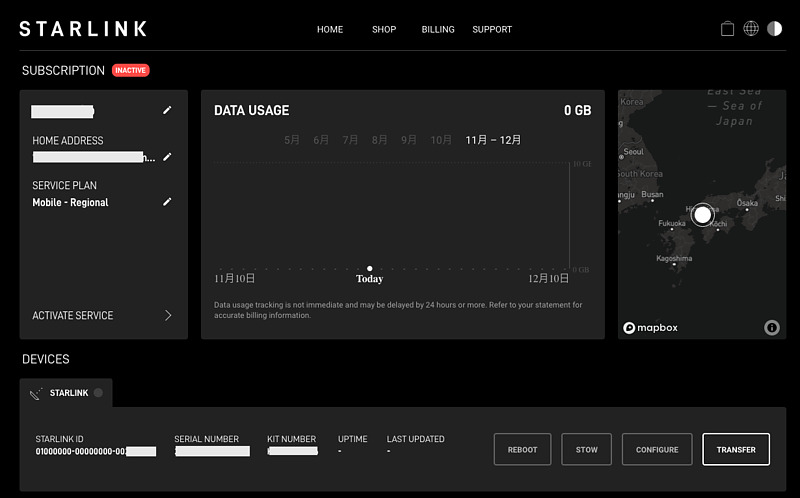
When you select activate service, a list of plans and fees will be displayed. The monthly usage fee for the Mobile-Regional plan (old RV plan) is 9,900 yen, but a pro-rated fee of 5,602 yen is presented from the restart date to the next usage period. You can now choose another plan when resuming.
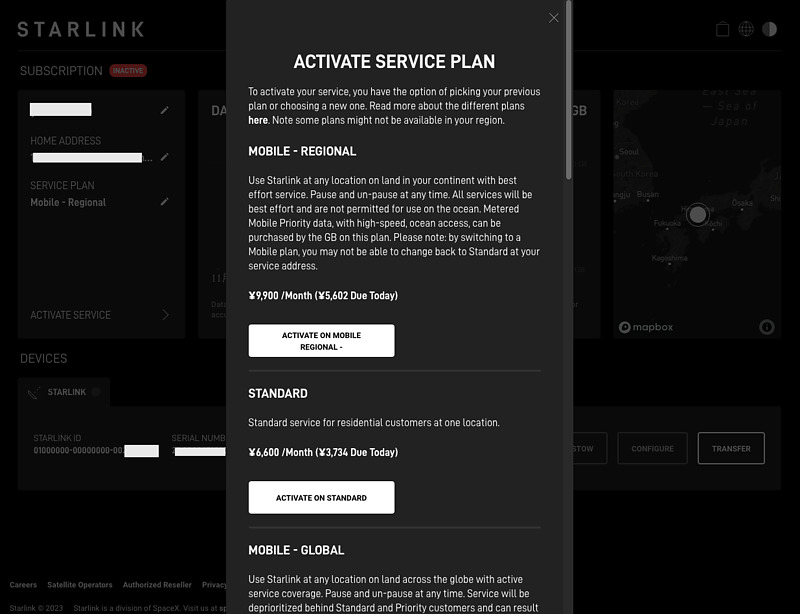
You can still change plans even after you resume usage. Here, since it is the day of reopening and no charges have been made yet, the difference to the Standard plan (formerly Residential plan) is also displayed as 0 yen.
Place the Starlink dish (antenna) in a place with a good line of sight, turn on the power, and wait for a while, and the contract information will be reflected and available for use.
Using bypass mode
Starlink’s internet connection typically uses Wi-Fi. Like home routers, Starlink’s Wi-Fi uses DHCP (dynamic host configuration protocol) to assign private addresses to connected PCs. Second generation rectangular dish antennas provides both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
You can make an Ethernet connection by purchasing the Ethernet adapter option. When I used this Ethernet adapter before, I couldn’t connect this adapter to the PC directly, so I used a hub. This time, I was able to connect the Ethernet adapter directly to the PC. I think it’s due to a firmware update.
Turn off this internal router for more advanced usage. In this bypass mode, Wi-Fi will be turned off automatically. Shifting to bypass mode is done from the settings screen of the dedicated app on the smartphone connected to Starlink Wi-Fi.
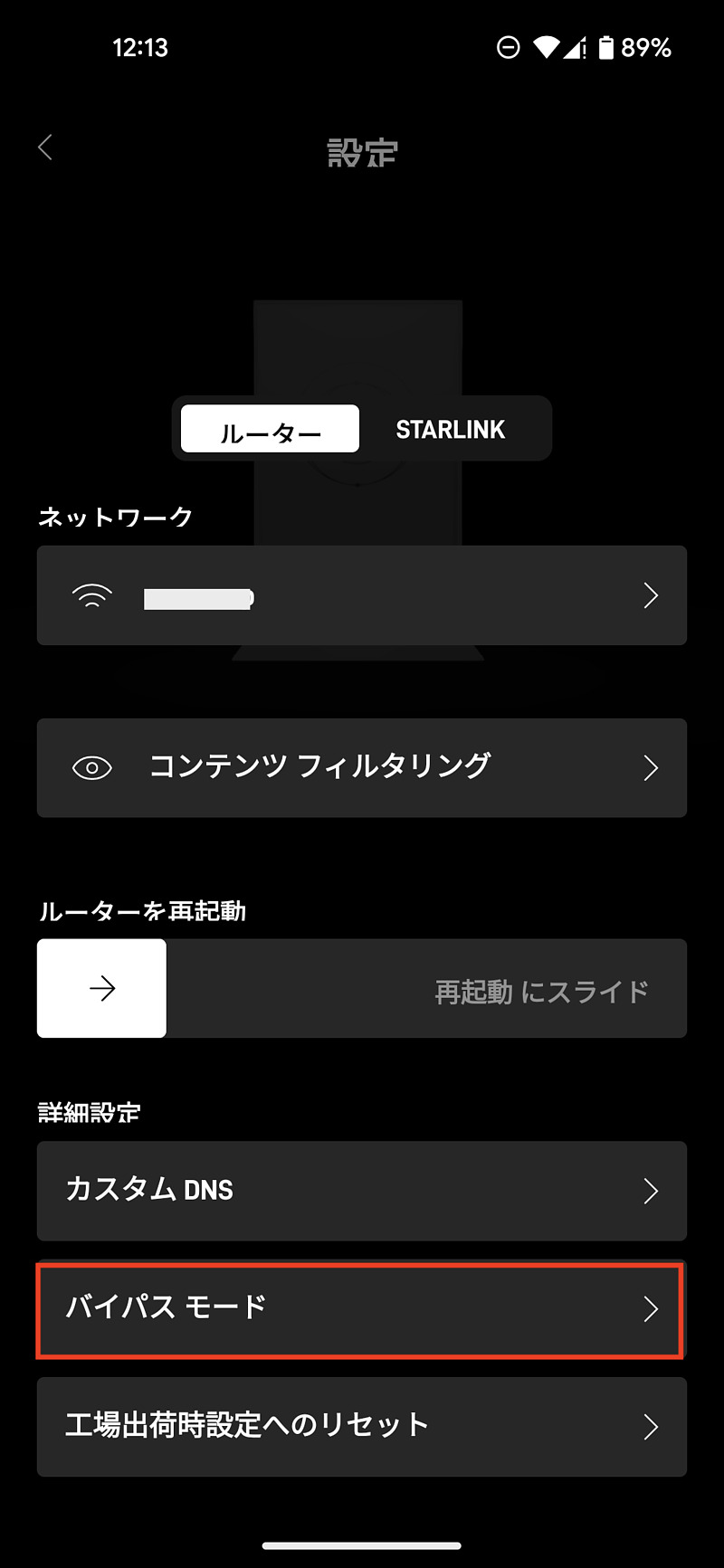
By touching this red line area, a confirmation screen will be displayed. This slide will turn off Wi-Fi and use Starlink over Ethernet from now on. To restore it, simply connect and disconnect the power repeatedly, and an animation display is also available.
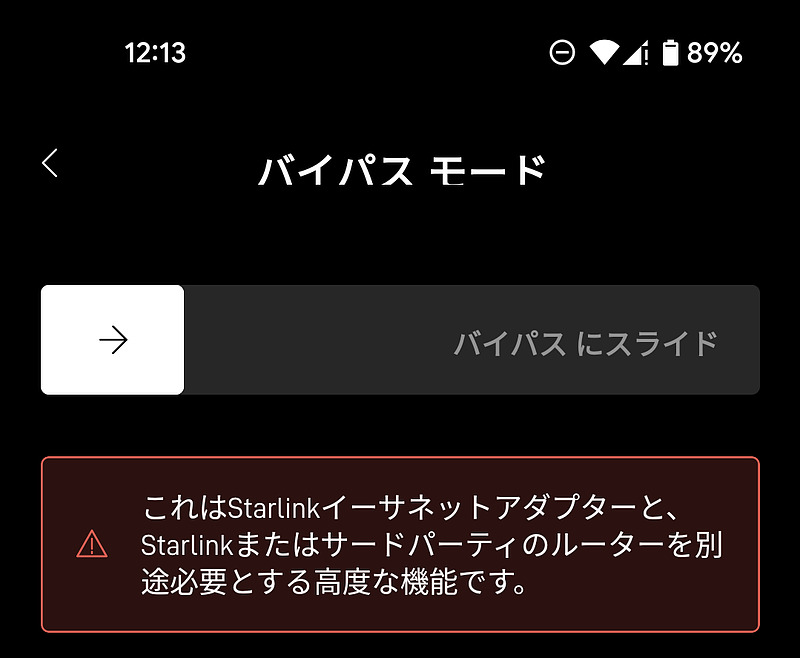
In my case, for some reason the transition to bypass mode failed. A questionnaire is also displayed. By performing the same operation again, I was able to transition to bypass mode.
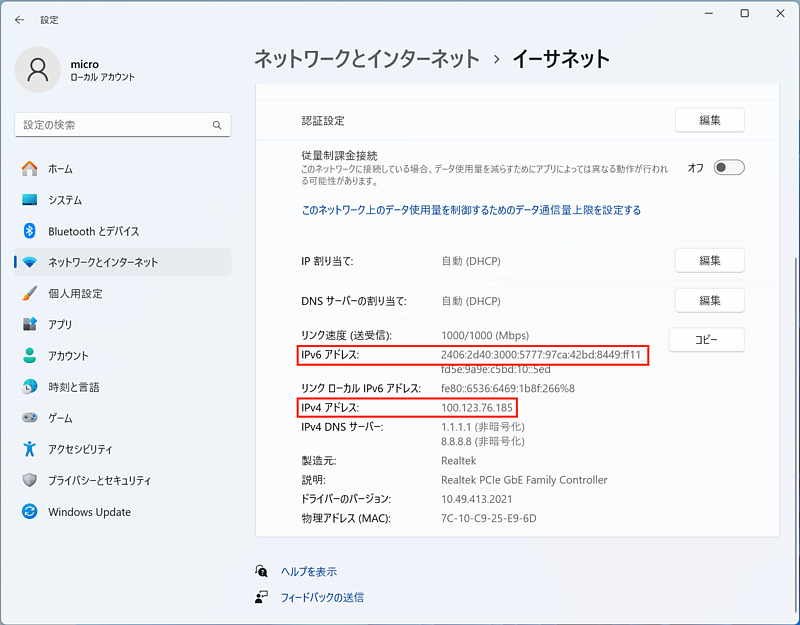
The PC connected to the Ethernet adapter was assigned an IPv6 address as well as a shared IPv4 address instead of a private IPv4 in normal mode. Similar to private IPv4 addresses, PCs assigned this IPv4 address can connect to the Internet, but cannot connect from the Internet. A shared IPv4 address is an address that is assigned more to the Internet than a private IPv4 address, and seems to allow for more simultaneous connections.
Remote access of Starlink using a microcomputer
According to Mr. Taniguchi’s article, I tried building a redundant VPN for 171 yen per month using Starlink and the cloud (in Japanese), we try to enable remote access of Starlink installed in a location with good visibility.
Using Raspberry Pi 3B as a microcontroller, we aim to use a firewall such as iptables, two-way remote use using wireguard VPN, and web access using a squid proxy server.
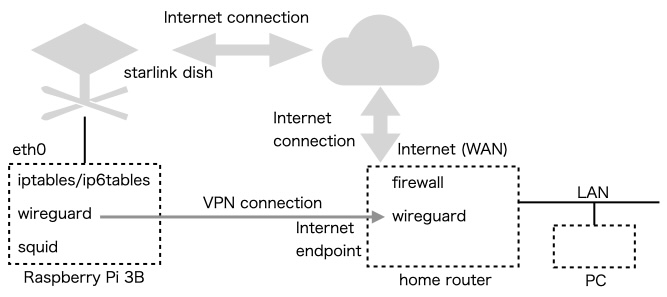
At the Starlink side, I connected Starlink and Raspberry Pi directly via Ethernet and supplied power to both. On the other hand of this home router side, the home router assigned a fixed IP address that could be connected to from the Internet, and it is assumed that ``wireguard’’ can be executed inside or outside the home router. Since it is not possible to connect from the Internet side to the starlink dish side, the VPN is a one-way connection from the starlink dish side to the home router side.
Also, to use the VPN, you will need to turn on IP forwarding in the Linux kernel. Knowledge of firewalls and the Internet is required. I can’t give you an example of how to set it up or disclose the internal address, as it would be a security hole.
The validity period of an IP address using DHCP is short, about 3 to 5 minutes. An example of an IP route assigned by DHCP to this Raspberry Pi is as follows.
$ ip r
default via 100.64.0.1 dev eth0 proto dhcp src 100.123.76.185 metric 99
xxx.xxx.xxx.0/24 dev wg0 scope link
34.120.255.xxx dev eth0 proto dhcp scope link src 100.123.76.185 metric 99
100.64.0.0/10 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 100.123.76.185 metric 99
192.168.100.1 dev eth0 proto dhcp scope link src 100.123.76.185 metric 99
$ ip -6 r
2406:2d40:3000:5777::/64 dev eth0 proto ra metric 99 pref medium
fe80::/64 dev eth0 proto kernel metric 1024 pref medium
default via fe80::200:5eff:fe00:101 dev eth0 proto ra metric 99 pref medium
In this example, a route is assigned to the mysterious IP address 34.120.255.xxx. This address changes frequently. When I checked the IP address here using the host command, I found that it was *.bc.googleusercontent.com, that of Google’s server.
You can remotely monitor the operating status of starlink dish by accessing http://dishy.starlink.com/ from the home router PC via squid. This IP address is a private address of 192.168.100.1 and has an IP route assigned by DHCP from starlink dish.
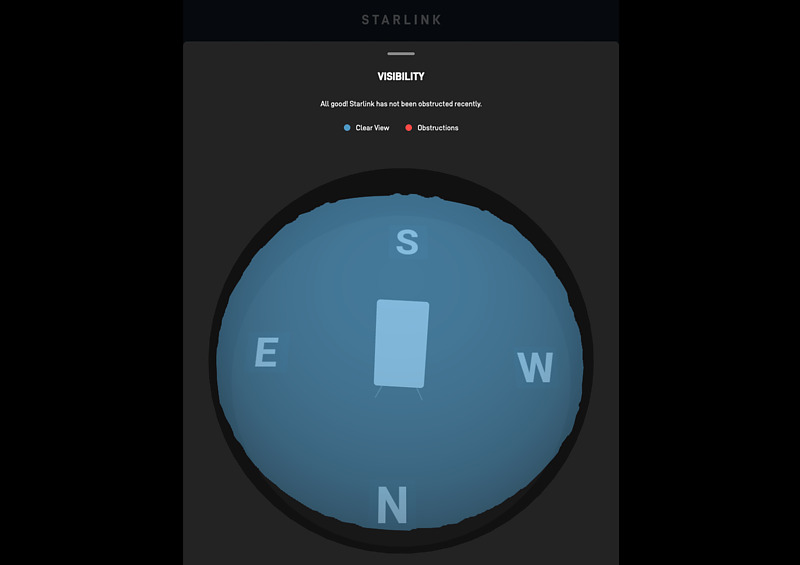
Unfortunately, the statistics information button is grayed out and unavailable in this display. The speed test button is also unavailable, leaving me with no way to evaluate speed between Starlink Dish and Starlink networks. Press the visibility button to display the starlink dish obstacle evaluation results. Here, visibility was rated almost perfect.
Let’s graph the delay time changes between the home router and starlink dish using SmokePing.
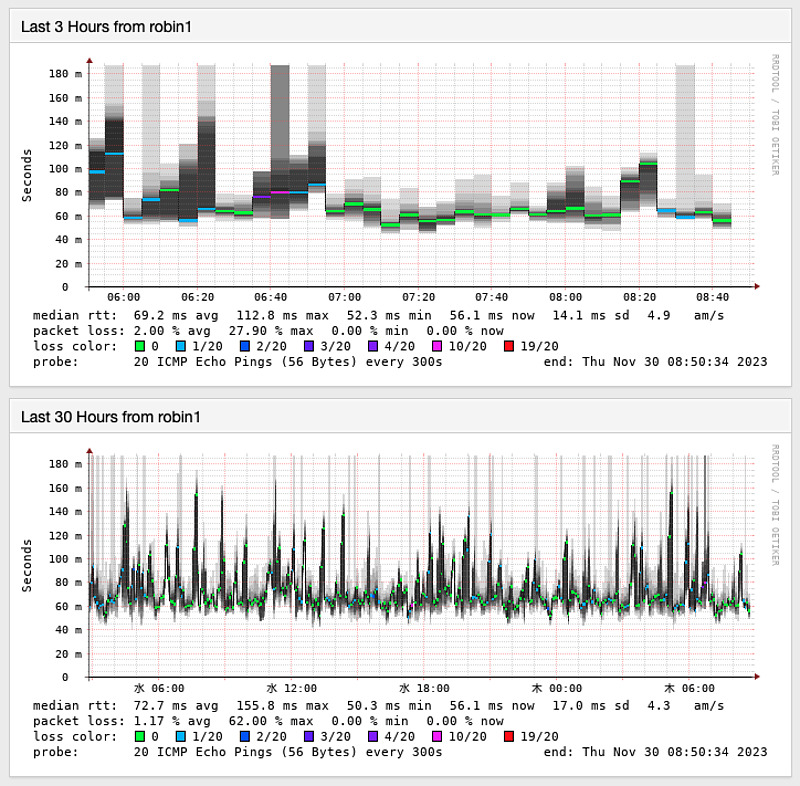
This is the statistics of the round trip time (RTT) from both ends of the VPN from the Starlink Dish installation location in Hiroshima to my home in Hiroshima.
The measurement method is to perform pings 20 times in a row, once every 5 minutes. Here, I am using an IPv6 address as the VPN route.
At times we have observed large RTTs of over 150 ms and large packet losses of around 50 percent, but most of the time we have seen RTTs of around 80 ms and packet losses of between 0 and 5 percent. I don’t think there will be any major problems with normal web browsing or video viewing.
Conclusion
I resumed using Starlink and tried using bypass mode remotely. There are no maintenance fees even when your plan is suspended, and we can now move between plans. Starlink is updated daily, so the content written here may become outdated quickly, but it doesn’t seem to be a bad thing for users. I think we are living in a better era as satellite internet is now available at low cost.
Related article(s):
- au Starlink Direct 24th October 2025
- Starlink Mini 10th April 2025
- Starlink Roam 50GB Plan 4th February 2025
- Starlink connection in an open environment 28th February 2023
- Starlink Ethernet adapter 15th February 2023
- I became a Starlink user 11st February 2023